Sustainable Health Practices: Improve Your Well-Being
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, the concept of sustainable health practices emerges as a pivotal approach to enhancing individual well-being and fostering a healthier society. By integrating wellness into daily routines, individuals can promote long-term health that not only benefits them personally but also contributes positively to community health. This multifaceted approach encompasses various dimensions, including diet, exercise, social relationships, and mental health, which are interdependent and significantly influence overall wellness. For instance, a holistic view of health incorporates the principles represented in the image of Lifestyle Psychiatry Domains , highlighting how aspects like social interactions and mindfulness collectively support mental health. As health practitioners and policymakers increasingly recognize the importance of sustainability, individuals are encouraged to embrace lifestyle changes that align with sustainable health practices to improve their well-being and that of future generations.
II. The Importance of Nutrition in Sustainable Health
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable health, as it directly influences individual well-being and community resilience. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, not only bolsters physical health but also communities socio-economic frameworks, impacting food security and environmental sustainability. A growing body of research supports the integration of nutrition-sensitive practices into agricultural methods, highlighting that innovative approaches like Nutrition-Sensitive Climate Smart Agriculture (NSCSA) can enhance food production while promoting better nutritional outcomes (Kızıldeniz Tefide et al.). Furthermore, addressing disparities in nutritional health, especially in urban environments, is crucial for combating childhood obesity and related health issues among vulnerable populations (Al-Khudairy et al.). Thus, improving nutrition is not solely a health concern; it is intrinsically linked to broader societal goals, necessitating a multifaceted approach that encompasses community engagement and sustainable practices. The relationship between nutrition and overall health is aptly summarized in , illustrating the various dimensions contributing to diet quality and well-being.
The image presents a circular diagram that illustrates the concept of ‘Diet Quality’ as a multifaceted subject. At the center of the diagram is an assortment of fresh fruits and vegetables, symbolizing healthy eating. Surrounding this central focal point are eight interconnected domains: Emotional, Social, Intellectual, Spiritual, Vocational, Physical, Financial, and Environmental. Each domain is visually represented by an associated icon, indicating the diverse factors that influence diet quality. This holistic approach underscores the impacts of various aspects of life on dietary choices and overall health, making it a useful graphic for understanding the complex interplay between diet and well-being.
Image1 : Diagram illustrating the multifactorial aspects of diet quality.
III. The Role of Physical Activity in Enhancing Well-Being
Physical activity is a cornerstone of enhancing well-being, acting as a vital component in the pursuit of sustainable health practices. Engaging in regular exercise not only improves physical fitness but also fosters mental health benefits by reducing anxiety and depression, while boosting mood and cognitive function. This dual impact underscores its importance in a holistic approach to well-being. Moreover, the integration of nature-based solutions within urban environments can further amplify these benefits, promoting sustainable practices that are both health-enhancing and ecologically sound (Cecchi et al.). For instance, urban green spaces encourage physical activity, encouraging a community-oriented approach that connects social interactions with health outcomes. This interconnectedness aligns with the holistic health model that emphasizes the relationship between physical activity and various dimensions of well-being, as illustrated in the diagram of Lifestyle Psychiatry Domains . Thus, promoting physical activity becomes not just a personal health decision but a community and environmental imperative.
IV. Mental Health and Sustainable Practices
The interplay between mental health and sustainable practices is crucial for cultivating overall well-being, particularly through the promotion of green and blue exercise. Engaging in physical activity within natural environments not only enhances fitness but also contributes to mental wellness, as these practices draw attention to the interconnectedness of ecological preservation and personal health. The World Health Organization emphasizes the significance of green and blue exercise in fostering holistic health, advocating for public policies that facilitate such opportunities (Calmeiro et al.). Additionally, addressing mental health issues, especially in vulnerable populations like incarcerated individuals, is integral to sustainable health outcomes (Anne van den Broek et al.). By incorporating practices that bolster mental health within sustainable frameworks, society can promote a healthier populace while simultaneously nurturing the planet. This holistic approach aligns with the principles of lifestyle psychiatry, which highlight systemic connections essential for effective health management .
The image presents a diagram illustrating the various domains of lifestyle psychiatry. It is organized as a circular chart, divided into six segments, each labeled with a specific domain: ‘Social Relationships,’ ‘Physical Exercise,’ ‘Diet & Nutrition,’ ‘Restorative Sleep,’ and ‘Mind-body and Mindfulness Practices.’ This visual representation emphasizes the interconnectedness of these aspects in promoting mental health and well-being. The title ‘Lifestyle Psychiatry Domains’ indicates a focus on how lifestyle choices impact psychiatric health, making it relevant for discussions on holistic approaches to mental health care.
Image2 : Diagram of Lifestyle Psychiatry Domains.
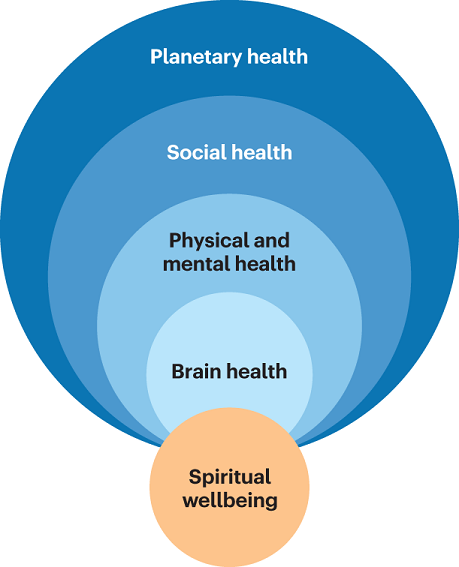
In conclusion, adopting sustainable health practices is not merely a trend but a vital strategy for enhancing personal well-being and promoting a healthier society. The interconnected nature of various health dimensions, as illustrated in the concentric circles of , highlights how our physical, mental, and social health are intertwined with the choices we make daily. By prioritizing aspects such as nutritious eating, physical activity, and social relationships, individuals are more likely to experience holistic improvements in their overall quality of life. As we transition towards more sustainable practices, including those promoting active mobility and mental health, the collective impact on community health becomes evident. Ultimately, fostering these habits not only benefits individual practitioners but also cultivates a culture of well-being that resonates across generations. Thus, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle choices is essential in the pursuit of sustainable health for everyone.
The image presents a visual representation of the interconnectedness of various health dimensions, organized into concentric circles. At the outermost layer is ‘Planetary health’, followed by ‘Social health’, and then ‘Physical and mental health’. The innermost circle is ‘Brain health’, which is situated within the overarching context of the system. At the center of this model is ‘Spiritual wellbeing’, depicted as a separate but crucial component. This visualization emphasizes the holistic approach to health, suggesting that individual health dimensions are interdependent and contribute collectively to overall wellbeing.
Achieving Optimal Health the Organic Way, Science Behind Acupuncture and Its Benefits
References:
Kızıldeniz Tefide, Mekyassi Hiba. “The role of nutrition-sensitive climate-smart agriculture in ensuring global food security”. EDP Sciences, 2024, https://core.ac.uk/download/599170214.pdf



