Discover Inspiring Organic Living Ideas
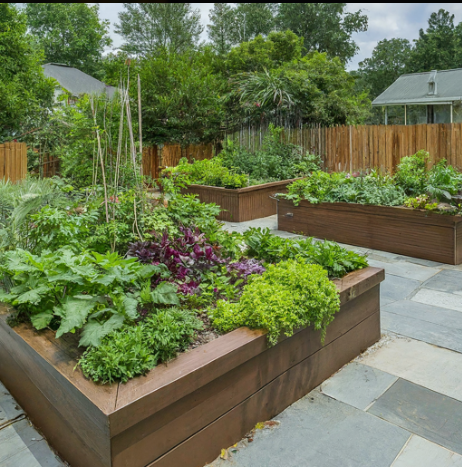
In recent years, the movement towards organic living has gained momentum, inspiring individuals to adopt sustainable practices that not only benefit personal health but also contribute positively to the environment. The quest for organic solutions involves a deep understanding of our interconnectedness with nature, as well as a commitment to fostering biodiversity and resilience within our ecosystems. For instance, the utilization of strategic imagery can enhance awareness of ethical farming practices, as discussed in research highlighting the importance of visual elements in promoting sustainable futures, such as (Patzel et al.). Furthermore, workshops like those conducted by the European Multifunctional Farmers Network exemplify collaborative efforts that merge education and practical strategies for organic farming, supporting the idea that community engagement is pivotal in this movement (Alebeek et al.). As we explore inspiring organic living ideas, these foundational concepts serve to illuminate the broader implications of our choices in both urban and rural settings, inviting us to rethink our relationship with the environment. The vibrant scene captured in reinforces the theme of urban gardening as a vital aspect of sustainable living, showcasing how accessible such practices have become.
A. Definition and Importance of Organic Living
Organic living is defined as a lifestyle that prioritizes the use of natural products, sustainable practices, and a conscious approach to the environment. This paradigm not only promotes physical health through the consumption of organic food free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, but it also fosters a deeper connection to nature and community. As highlighted in the findings of the Organic Revision project, key values associated with organic living include food quality, environmental health, and livelihood, demonstrating that such a lifestyle is integral to both individual wellness and ecological sustainability (Roviglioni et al.). Furthermore, initiatives like those of Be The Change illustrate how organic living can empower communities to engage in sustainability practices, thereby amplifying collective impact (Rosenbaum et al.). The visual representation of thriving urban gardens in reinforces the practicality and aesthetic appeal of organic living, emphasizing its role in enriching urban spaces while supporting biodiversity.
II. Benefits of Organic Living
The transition to organic living is often celebrated for its multifaceted benefits, addressing personal health, environmental sustainability, and economic considerations. Engaging in organic agriculture promotes biodiversity and enhances soil health, which not only improves crop yields but also supports ecological balance within local environments. As the global audience seeks more sustainable consumption practices, understanding the implications of their choices becomes crucial; this aligns with the findings presented at the international conference on sustainable consumption ((Balmer et al.)). Furthermore, organic living can lead to community empowerment and local food systems through urban gardening initiatives, which enhance food security and foster social connections. Urban gardens, such as those illustrated in , exemplify these principles by showcasing how accessible gardening can yield nutritious produce while instilling a sense of shared responsibility towards our environment. Thus, embracing organic living serves as a vital stepping stone toward achieving a healthier and more sustainable future ((Commission SD)).
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
| Health | Reduced exposure to synthetic pesticides and chemicals | Lower risk of certain health issues |
| Environment | Promotes biodiversity and soil health | Reduced pollution and ecosystem damage |
| Taste | Often more flavorful produce | Enhanced culinary experiences |
| Animal Welfare | Higher standards for livestock treatment | Improved quality of life for farm animals |
| Sustainability | Focuses on long-term ecological balance | Helps preserve resources for future generations |
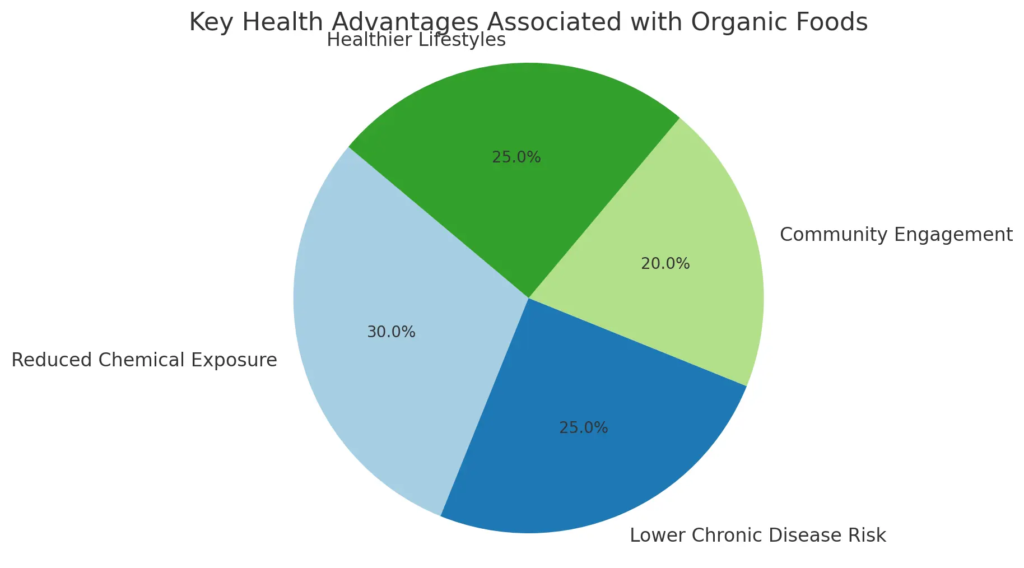
A. Health Advantages of Organic Foods
The health advantages of organic foods extend beyond basic nutrition, encompassing broader implications for individual well-being and environmental sustainability. Organic foods are cultivated without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which reduces exposure to harmful chemicals and can lead to lower risks of chronic diseases among consumers. Moreover, the local food movement underscores the importance of community engagement in fostering healthier eating habits, as highlighted by the promotion of local food chains that offer fresher, more nutritious options while also supporting local economies (Morely et al.). In-depth qualitative studies demonstrate that consumers who prioritize organic options often adopt healthier overall lifestyles, influenced by their understanding of the benefits associated with organic consumption (Ayres et al.). Thus, embracing organic foods not only contributes to personal health but also aligns with an ethos of responsible consumption that benefits society as a whole, creating a sustainable future.
III. Sustainable Practices in Organic Living
Sustainable practices in organic living are paramount for fostering environmental health and food security, especially in the context of escalating global challenges. Organic farming emphasizes ecological processes that promote biodiversity while simultaneously enhancing soil fertility through methods such as composting and intercropping. These practices are not only beneficial for the environment but also empower small-scale farmers, who often lack access to financial and natural resources, to improve their livelihoods while adhering to principles of sustainability (cite9). Notably, initiatives like Farmer Field Schools facilitate knowledge sharing among farmers, enabling them to adopt agro-ecological methods effectively (cite10). Such communal learning further inspires local communities to engage in sustainable agriculture, as evidenced by gardens that prioritize resilience and biodiversity, illustrated in the vibrant image displaying sustainable garden practices with lush greenery and organized beds . Hence, sustainable organic living embodies a holistic approach that connects ecological health with socioeconomic growth.
A. Eco-Friendly Gardening Techniques
Incorporating eco-friendly gardening techniques is essential for cultivating sustainable living practices that not only enhance the gardens productivity but also contribute positively to the environment. Techniques such as companion planting, organic mulching, and rainwater harvesting promote biodiversity and reduce reliance on chemical inputs, thereby fostering a healthier ecosystem. As urban areas expand, the significance of sustainable practices in gardening becomes even more pronounced, serving as a model for eco-communities that prioritize environmental education and awareness ((Pathiraja et al.)). The vibrant scenes of urban gardens, especially those displayed in images like , underscore the potential of local food production in mitigating ecological footprints while encouraging community engagement. These methodologies align with notions of ecological activism, emphasizing the role of individual gardeners in advocating for environmental stewardship ((Thiebot et al.)). By embracing these techniques, we lay the groundwork for a resilient future and inspire collective efforts toward organic living.
The journey toward embracing organic living is not merely a shift in agricultural practices; it embodies a holistic paradigm that inspires a profound connection between individuals, communities, and the environment. As the evidence suggests, organic farming enhances food security while addressing vital issues such as soil health and biodiversity, ultimately contributing to sustainable development goals that align with a vision of global equity and environmental stewardship (Jacobsen et al.). Furthermore, the application of innovative approaches, such as Farmer Field Schools, facilitates knowledge sharing among farmers, empowering them to adopt practices that are both eco-friendly and economically viable (Dewulf et al.). Illustrative of these efforts, images like the vibrant urban garden exemplify the practical application of sustainable gardening methods that foster resilience and productivity in local communities. As we champion such inspiring organic living ideas, we lay the groundwork for a sustainable future driven by ecological harmony and mindful consumption.
A. The Future of Organic Living and Its Impact on Society
The future of organic living is poised to significantly reshape societal norms and practices, particularly as awareness of environmental sustainability grows. Embracing organic lifestyles promotes a deeper connection with nature, as individuals engage in practices that support biodiversity and reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals. This shift not only fosters sustainable consumption patterns, essential for addressing the environmental consequences of traditional agriculture, but also enhances community resilience against challenges posed by climate change. For example, as indicated by the emphasis on “Sustainable Gardening” and “Biodiversity” in the image featuring lush garden scenes , urban spaces are increasingly integrating organic practices that promote ecological health. This transformation reflects a broader societal trend towards reconceptualizing consumption and cooperation among diverse stakeholders, a theme underscored in academic discussions surrounding sustainable consumption patterns (Balmer et al.). Ultimately, these changes signal a pivotal move towards a more harmonious relationship with our environment.