Elevate Your Wellness with Organic Nutrition Options
Organic Nutrition and Its Benefits – The increasing attention on organic nutrition reflects a growing recognition of its pivotal role in enhancing personal and environmental health. Organic foods, cultivated without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, provide a broader spectrum of nutrients while minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals. This shift toward organic consumption not only supports healthier dietary choices but also contributes to sustainable farming practices that are less detrimental to ecosystems. A holistic approach to nutrition emphasizes the interconnectedness of food choices and overall wellness, underscoring the psychological benefits of consuming whole, organic produce. Furthermore, the illustration of how these choices impact mental health exemplifies the complex relationship between nutrition and well-being, reinforcing the notion that food is foundational to a balanced lifestyle. This discussion is well-supported by , which highlights the relationship between diet and mental health, further enhancing the significance of organic nutrition in elevating overall wellness.
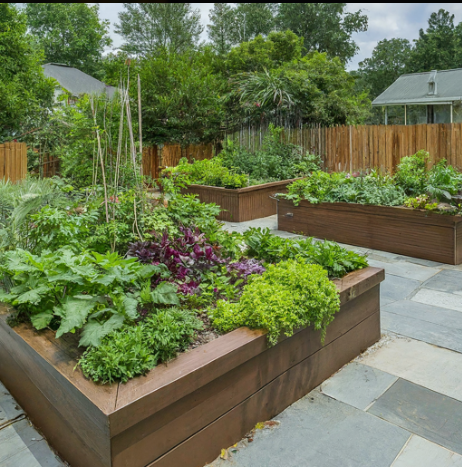
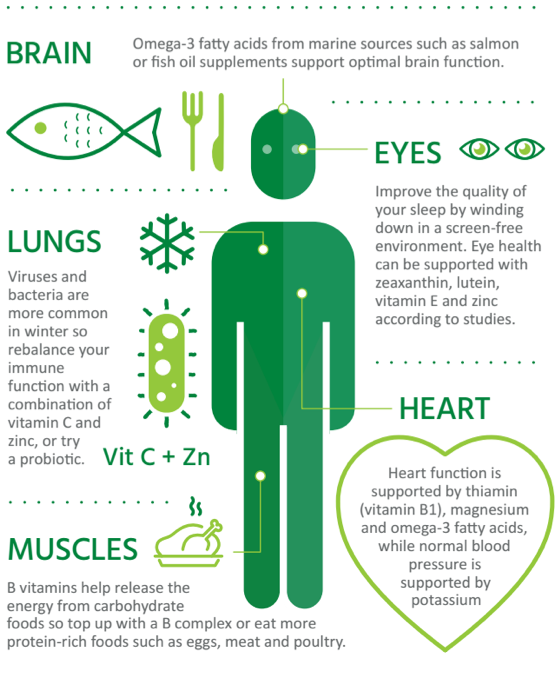
II. The Impact of Organic Foods on Physical Health
The consumption of organic foods has gained traction as a pivotal factor in enhancing physical health, primarily due to their nutritional benefits and reduced exposure to harmful chemicals. Organic agriculture avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, thus potentially decreasing health risks associated with chemical residues, which are often linked to a range of health issues, including endocrine disruption and cancer (Winterfeld A et al.). Furthermore, research indicates that organic foods are perceived by many consumers as healthier, reflecting a growing societal inclination toward health and wellness motivations in dietary choices (Andrade et al.). This increasing preference for organic options can be linked to the broader notion of holistic health, which recognizes the interplay between diet and overall well-being (Admin). Thus, fostering a commitment to organic nutrition may not only contribute to individual health but also promote sustainable agricultural practices, aligning physical health with environmental stewardship. An illustration of this transformative relationship is depicted in , emphasizing the necessity for a healthier agri-food system.
III. Mental Wellness and the Role of Organic Nutrition
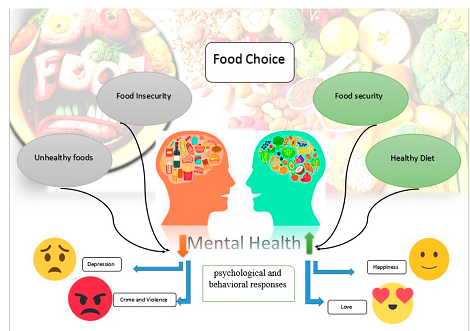
The intersection between organic nutrition and mental wellness has garnered increasing attention, highlighting the profound impact dietary choices can have on psychological health. Recent studies indicate that organic foods, which are devoid of harmful pesticides and additives, contribute not only to physical vitality but also to emotional and mental resilience. For instance, incorporating organic produce enhances nutrient intake, which is crucial for optimal brain function and the regulation of mood-related neurotransmitters. Research emphasizes the role of urban agriculture, as growing food in community spaces fosters social connections while promoting mental well-being ((Anne C Bellows et al.)). Engaging with nutritious, organic options inherently supports holistic health, reinforcing the understanding that mental and physical wellness are interlinked. A visual representation of this relationship can be seen in , which demonstrates how food choices affect mental health outcomes, thereby underscoring the necessity of integrating organic nutrition into wellness strategies. In sum, fostering organic nutrition paves the way to enhanced mental wellness, positioning diet as a pivotal element in the broader framework of health.
The image illustrates the relationship between food choices, mental health, and psychological responses. Central to the diagram is the concept of ‘Food Choice,’ surrounded by factors such as ‘Food Insecurity,’ ‘Food Security,’ and ‘Healthy Diet.’ There are visual representations of unhealthy foods, with arrows indicating the influence of these factors on mental health, leading to social behaviors and emotional states, including depression, crime and violence, happiness, and love. The background features various food items, further emphasizing the theme of dietary choices and their implications for mental health.
Image1 : Relationship between Food Choice and Mental Health
IV. Sustainable Practices in Organic Farming
Sustainable practices in organic farming emphasize holistic methods that prioritize environmental health and biodiversity, facilitating both immediate and long-term benefits for ecosystems and communities. By utilizing diverse crop rotation, organic farmers can enhance soil quality and reduce reliance on synthetic fertilizers, which correlates with findings that underscore agricultures adverse impacts on essential ecosystem services (Hidayati et al.). Moreover, urban agriculture initiatives exemplify how engaging communities through local food production can bolster individual well-being and food security, ultimately promoting healthier lifestyles (Anne C Bellows et al.). This integration of sustainable practices not only supports ecological balance but also fosters a deeper connection between consumers and the food system, as evidenced by the growing public interest in organic and locally sourced produce (Admin). The visual representation of interrelated health dimensions, as shown in , further reinforces the argument that sustainable organic farming can yield positive mental, social, and physical health outcomes in society.
The image presents a conceptual diagram illustrating the interconnected dimensions of health, comprising mental, social, physical, spiritual, and financial health. Each dimension is accompanied by specific components that contribute to overall well-being. The central message emphasizes the importance of recognizing the interconnections among these health dimensions, particularly in the context of treating complex conditions such as hypertension within immigrant populations. The diagram serves to highlight how a holistic approach to health can enhance understanding and management of various health issues.
In conclusion, embracing organic nutrition is not merely a dietary choice but a holistic commitment to enhancing overall wellness. As evidenced throughout this essay, the integration of organic foods into one’s diet supports physical health, mental clarity, and environmental sustainability. The impact of these choices extends beyond personal well-being, reflecting a broader responsibility towards community health and ecological balance. For instance, visual representations like illuminate the transformative potential of organic farming practices, showcasing how they address critical issues such as malnutrition and climate change. By prioritizing organic options, individuals empower themselves to engage in a lifestyle that fosters not only individual wellness but also contributes positively to societal health. Ultimately, elevating one’s wellness through organic nutrition options exemplifies a proactive approach to living healthily, responsibly, and sustainably, revitalizing both the individual and the planet.
References:
- Amy Winterfeld, Douglas Shinkle, Larry Morandi. “Promoting Healthy Communities and Reducing C
- Admin. “Wellness Tips for Beginners: Get Started on a Healthier”. Well Health Organically, 2025, https://wellhealthorganically.in/category/organic-living/