Organic Food Choices Nourish Your Body Protect the Planet
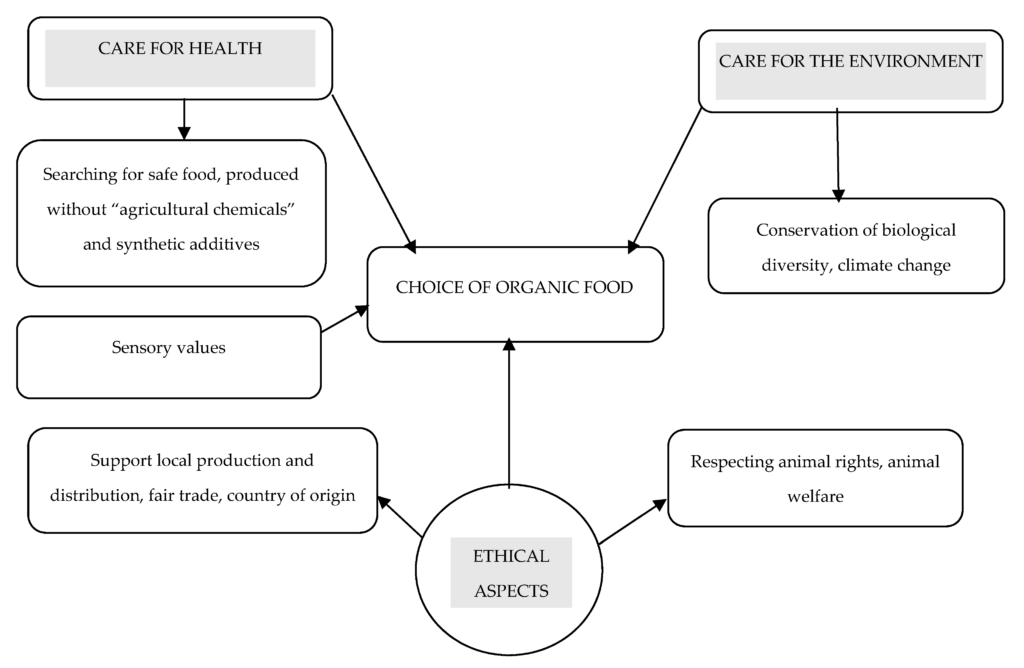
In recent years, the increasing awareness of health and environmental issues has prompted more consumers to consider organic food choices as integral to nurturing both personal well-being and planetary health. The connection between organic food production and sustainable dietary practices is evident, as these choices often mitigate harmful agricultural practices that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and soil degradation. For instance, a study shows that the primary source of emissions in food production stems from cultivated soil, highlighting a significant area for improvement through organic methodologies (Helenius et al.). Furthermore, sustainability labelling is gaining traction, with consumers increasingly recognizing the role of food choices in promoting eco-friendly practices (Brown et al.). This shift not only reflects a heightened consumer consciousness but also aligns with societal efforts to foster sustainable food systems. To illustrate this point further, presents the motivations behind organic food consumption, showcasing the intertwined benefits of health and environmental consciousness.
A. Overview of organic food and its growing popularity
The rising popularity of organic food reflects a substantial shift in consumer preferences towards healthier and more sustainable choices. As awareness about the impact of conventional agricultural practices grows, consumers are increasingly drawn to organic products that promise reduced exposure to harmful pesticides and chemical fertilizers. This shift is not merely a trend; it signifies a broader movement towards environmental consciousness and public health. The demand for organic food is also influenced by changing trade dynamics and regulatory environments, as highlighted in recent literature, which underscores the push for organic farming practices to achieve a more significant role alongside traditional agricultural standards (Giovannucci et al.). Additionally, the efforts of local communities to address public health challenges through more equitable food systems are gaining traction, with innovative approaches emerging across the nation (N/A). Together, these factors illustrate a conscientious evolution in food choices that not only nourishes individual bodies but also safeguards the planet.
II. Health Benefits of Organic Food
The health benefits of organic food extend beyond improved nutrition to foster a holistic approach to well-being. Consuming organic products often reduces exposure to harmful pesticides and synthetic additives, which aligns with a growing awareness of food safety among consumers . Studies suggest that organic food may contain higher levels of essential nutrients, including vitamins and antioxidants, thereby enhancing immune function and overall health. Furthermore, organic farming practices emphasize biodiversity, a factor beneficial not only for personal health but also for ecological stability (Elliott et al.). The publics interest in these health advantages mirrors concerns about environmental degradation exemplified by incidents like the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, which starkly illustrated the consequences of industrial practices on ecosystems (Charles H Peterson et al.). Thus, choosing organic foods not only nourishes the body but also supports sustainable agriculture, contributing to a healthier planet.
| Nutrient | Organic | Conventional | Percentage Difference |
| Antioxidants | Higher | Lower | 20-40% more |
| Vitamin C | Higher | Lower | 27% more |
| Iron | Higher | Lower | 21% more |
| Magnesium | Higher | Lower | 29% more |
| Phosphorus | Higher | Lower | 14% more |
A. Nutritional advantages of consuming organic produce
The choice to consume organic produce not only supports personal health but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices. Research indicates that organic fruits and vegetables, cultivated without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, often contain higher levels of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, when compared to their conventional counterparts. This nutritional advantage is tied to the healthier soil and ecological practices employed in organic farming, which foster richer nutrient profiles in the crops produced. Moreover, the Powys Public Procurement Partnership highlights the correlation between sustainability and health outcomes, emphasizing that the integration of organic produce into public meal programs can yield significant benefits for both personal well-being and environmental stewardship (Anon). As consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental challenges associated with traditional agriculture, including greenhouse gas emissions, the shift toward organic options reflects a growing understanding of food’s role in ecosystem conservation (Østergård et al.). In essence, selecting organic produce not only nourishes the body but also aligns with a broader commitment to protect the planet. The image illustrating the environmental effects of vegetable oils serves as a compelling reminder of the broader implications of dietary choices on health and sustainability .
III. Environmental Impact of Organic Farming
The environmental impact of organic farming is increasingly recognized as a crucial factor in the discourse surrounding sustainable agriculture. By eschewing synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic farming practices foster healthier ecosystems, enhance soil resilience, and promote biodiversity, thus contributing to a sustainable agricultural framework. This paradigm shift is not just necessary for environmental stewardship but also vital in mitigating challenges such as land degradation and climate change. Moreover, studies indicate that adopting organic methods can significantly reduce the reliance on harmful agrochemicals while improving crop yields and soil health, especially in developing nations like Pakistan (Ali et al.). Additionally, by utilizing agricultural waste, such as straw, as organic fertilizers, farmers can further enhance soil fertility while curbing environmental pollution (Vardia et al.). Collectively, these practices position organic farming as a viable solution to the pressing environmental challenges of our time, making it an attractive choice for conscientious consumers.
A. How organic farming practices contribute to sustainability
Organic farming practices play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by fostering biodiversity, enhancing soil health, and reducing environmental impacts associated with traditional agricultural methods. By prioritizing natural inputs and crop rotation, organic farms can cultivate resilient ecosystems that support a variety of wildlife and plant species, which is critical for maintaining ecological balance. Moreover, these practices contribute to soil fertility through the organic matter left behind, ultimately leading to reduced dependency on chemical fertilizers, as highlighted by industry analyses of organic trends over the decades (Kristiansen et al.). Additionally, consumer behaviors surrounding organic food choices reflect a growing awareness of ecological responsibility, as seen in the narratives surrounding food sourcing and sustainability (Ayres et al.). The cumulative impact of organic farming on these various levels underscores its significance in fostering not just a viable agricultural system but also a healthier planet, thereby aligning consumer choices with environmental stewardship.
The intersection of health and environmental stewardship underscores the significance of organic food choices in contemporary society. By prioritizing organic products, consumers actively contribute to reducing harmful agricultural practices that jeopardize both personal well-being and the planets ecological balance. Such choices not only nourish individuals by eliminating synthetic additives and promoting natural eating patterns, as illustrated in , but also mitigate the environmental burden associated with conventional farming methods. The data from eco-labels further reveals how consumer behavior can be influenced to enhance eco-friendly purchasing practices, paving the way for sustainable consumption (Czarnezki et al.). Moreover, the economic implications of supporting organic agriculture demonstrate its viability as a market alternative that contributes positively to local economies and ecological health (Rousseau et al.). Ultimately, organic food choices emerge as a powerful means for individuals to foster both personal health and planetary protection.
A. The importance of making informed food choices for personal health and environmental protection
Informed food choices are pivotal not only for individual health but also for the broader spectrum of environmental sustainability. The increasing awareness regarding the health benefits of organic food has fostered a community of consumers who prioritize nutrition and ethical food sources. Regular consumers tend to trust organic products, believing them to be both healthier and tastier, fostering a shift in dietary habits that aligns with personal well-being and environmental stewardship (Bracchi et al.). Moreover, eco-labels, designed to enhance sustainable consumer choices, play a crucial role in guiding individuals towards greener options by elevating awareness and social accountability (Czarnezki et al.). By understanding the ecological and health implications of their purchases, individuals can effectively contribute to a sustainable food system. This community-oriented approach to food choices ultimately nourishes both body and planet, reinforcing the necessity for informed decision-making in todays consumer landscape .