Unlock the Power of Organic Products for Optimal Health
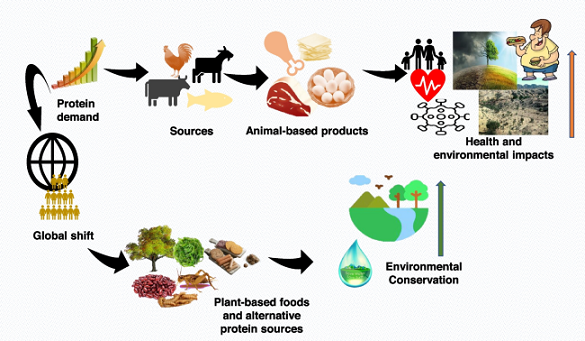
Organic Products and Their Health Benefits – The increasing popularity of organic products reflects a growing awareness of their substantial health benefits, which are intricately linked to holistic well-being. In contrast to conventional farming practices that often rely on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic agriculture embraces natural processes, thereby enhancing nutrient-rich soil and fostering biodiversity. This method not only mitigates harmful chemical exposure but also results in produce that is typically higher in antioxidants and vitamins, which have been associated with reduced risk of chronic diseases. Furthermore, the cultivation of organic products aligns with sustainability goals, as it promotes environmentally friendly practices and supports local economies. The relevance of these interconnections is underscored in , which illustrates the framework for sustainable plant-based diets, emphasizing the intricate relationship between health, nutrition, and ecosystem preservation. By unlocking the potential of organic products, individuals can make informed choices that contribute to their health and the planets future.
II. Nutritional Advantages of Organic Foods
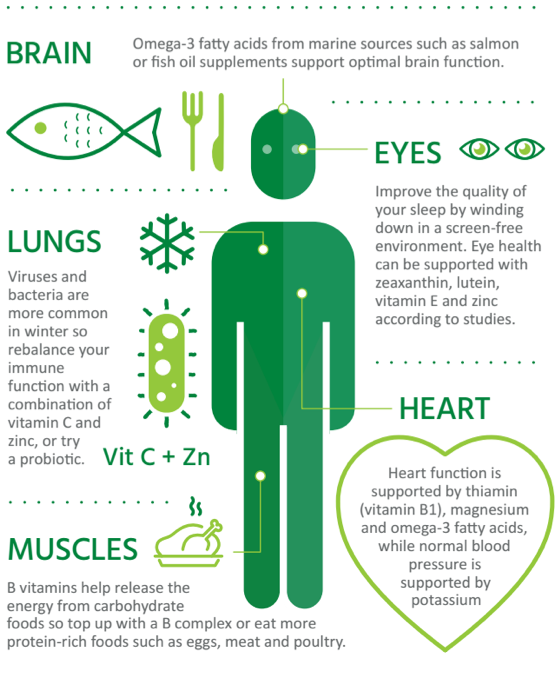
Organic foods offer a distinct array of nutritional advantages that promote overall health and well-being. Research indicates that consumers of organic products may experience improved health outcomes, attributed to higher concentrations of beneficial plant secondary metabolites and healthier fatty acid profiles in organic milk, which can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular conditions and cancer (Brandt et al.). Additionally, the diverse crop rotations employed in organic farming contribute to a more balanced nutrient composition in grains, enhancing their nutritional value (Brandt et al.). This is particularly relevant in the context of an increasing shift towards plant-based diets, which has been identified as a significant factor for climate mitigation, further underscoring the importance of organic foods in promoting sustainable dietary practices . The compelling evidence surrounding the enhanced nutritional profile of organic foods not only affirms their health benefits but also underscores their potential role in fostering a healthier population.
The image presents a conceptual framework for ‘Sustainable Plant-Based Diets,’ highlighting four main components: ‘Nutritionally adequate, healthy, safe’; ‘Protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems’; ‘Economically fair, accessible and affordable’; and ‘Culturally acceptable.’ Each component is accompanied by related health policies, such as food fortification, nutrition dissemination, and reductions in food waste, illustrating a comprehensive approach to integrating sustainability within dietary practices. This visual representation serves as a guide for policymakers and researchers focusing on public health, nutrition, and environmental sustainability.
Image1 : Framework for Sustainable Plant-Based Diets and Related Health Policies
III. Environmental Impact of Organic Farming
The environmental impact of organic farming is notably more favorable compared to conventional agricultural practices, making it a compelling focus for those seeking sustainable food sources. Organic farming emphasizes biodiversity, soil health, and reduced chemical usage, which contribute to enhanced ecosystem resilience. This method promotes a symbiotic relationship with the environment, often yielding lower greenhouse gas emissions than intensive monoculture systems, as evidenced by the strategic advantages laid out in various research agendas aimed at improving organic practices (Bügel et al.). Furthermore, the Saudi Arabian context illustrates the potential for organic farming to bolster local sustainability efforts, highlighting its significance in addressing agricultural challenges (Ghamdi A et al.). As consumers increasingly prioritize environmental health, organic farming emerges as a pivotal player in mitigating climate hazards, thereby enhancing both food security and overall public health, as depicted in discussions about the interconnectedness of dietary choices and environmental sustainability .
IV. Economic Considerations of Choosing Organic Products
The economic implications of choosing organic products extend beyond mere consumer spending, affecting a broader agricultural landscape. Organic farming often entails higher costs for production due to labor-intensive practices, stringent certification processes, and lower yields when compared to conventional methods. Nevertheless, these challenges can result in sustainable economic benefits, including healthier ecosystems and stronger local economies as consumers increasingly value the positive environmental impact of organic farming. The demand for organic products can stimulate market growth, leading to competitive pricing and improved accessibility over time, as evidenced in demand and price analysis (Rousseau et al.). Furthermore, Multi-Criteria Analysis (MCA) can assist consumers in navigating the complexities of organic versus conventional products, emphasizing the holistic nature of decision-making in food choices (Christensen et al.). Incorporating sustainable practices as illustrated in , which promotes diversified cropping systems, not only enhances food security but also contributes to economic resilience.
The image presents a conceptual diagram comparing two agricultural practices: intensified cereal monoculture and diversified rotation systems. It emphasizes the social, economic, and environmental benefits derived from crop management strategies. Key components include the processes involved in intensified monoculture, such as irrigation, fertilization, and transport, along with associated greenhouse gas emissions quantified in terms of Global Warming Potential (GWP). The diagram outlines the effects on soil health, nutrient cycling, and microbial diversity, illustrating how diversified rotation systems can lead to improved economic outcomes and reduced greenhouse gas footprints. The calculations for GWP direct and indirect emissions are also provided in the central area, highlighting their significance in evaluating agricultural impacts.
In conclusion, embracing organic products is not merely a personal health choice; it is a pivotal step toward sustainable environmental practices and enhanced food security. As the growing awareness of climate-related threats underscores the fragility of our food systems, transitioning to organic farming offers numerous benefits. Organic methods foster biodiversity, minimize chemical use, and enhance soil health, directly impacting both nutrition and environmental sustainability. Moreover, the shift towards these practices aligns with emerging dietary trends emphasizing plant-based options, as illustrated in . Such changes not only contribute to optimal health by offering nutrient-dense foods but also mitigate the ecological consequences of conventional agriculture. By prioritizing organic products, individuals can cultivate healthier lifestyles while simultaneously supporting agricultural systems that respect both people and the planet, thus unlocking the full potential of organic initiatives for future generations.